Tuli Research Centre for India Studies exhibition explores the Interplay between Indian Culture Nature and Animals.
New Delhi (India), April 13: At the India International Centre in New Delhi, the Tuli Research Centre for India Studies (T.R.I.S.) presents a captivating exhibition titled ‘Self-Discovery via Rediscovering India’, showcasing the vibrant tapestry of Indian art, cinema & cultural heritage with a focus on the intricate relationship between humans, nature and animals, particularly canine [...]


New Delhi (India), April 13: At the India International Centre in New Delhi, the Tuli Research Centre for India Studies (T.R.I.S.) presents a captivating exhibition titled ‘Self-Discovery via Rediscovering India’, showcasing the vibrant tapestry of Indian art, cinema & cultural heritage with a focus on the intricate relationship between humans, nature and animals, particularly canine children, or dogs in common parlance.
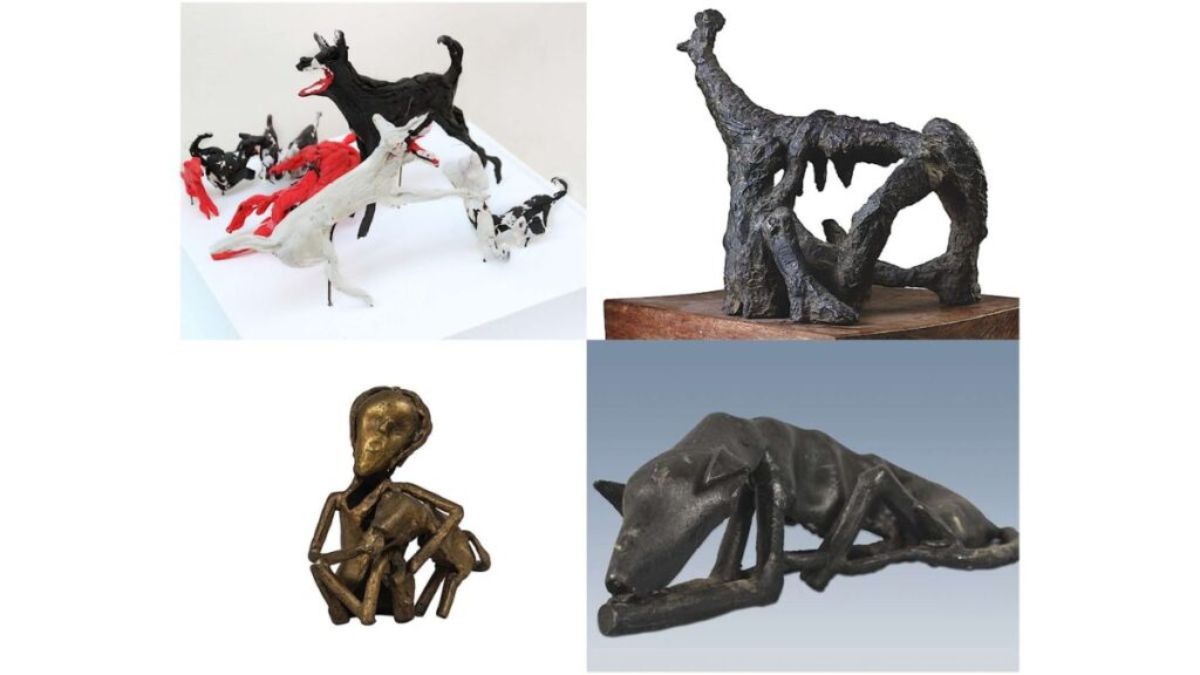
The striking oleograph by the Ravi Varma Press of Lord Dattatreya, the god of Pasupati, accompanied by four stray dogs is one example. The four dogs have been over the ages variously interpreted as symbolizing the four Vedas, or the four yugas, among other spiritual facets of the living consciousness. This ancient bond between human and canine reflects the deep respect accorded to dogs in Indian culture and Hinduism, recognizing them as eternal and compassionate companions.
In modern fine art, the dog has also been depicted with a blend of pain and joy, capturing the complexity of its relationship with humanity. Master artists such as Somnath Hore, Amit Ambalal, Debiprasad Roy Choudhury, Jyoti Bhatt, among others, have portrayed the dog with profound depth, reflecting the myriad emotions associated with this beloved creature.
However, amidst this celebration of the bond between humans and dogs, the exhibition tours sheds light on a sobering reality – the cruel treatment of stray street canine children by certain sections of society.
This gap between the reverence for dogs in Indian culture and religion and their treatment in contemporary society serves as a poignant reminder of the need for greater understanding and compassion. As Neville Tuli, the visionary behind the institution aptly observes, “The canine child, has always been the most respected companion of the human being, a true friend to the common man.
However, recently, with certain sections of society, who cannot understand or have not had the opportunity to love or be loved by the stray dog, their fears and paranoias dominate their thinking and actions, for few can speak effectively on behalf of the dog. Thus, any minor menace, however rare, is easily blown up and distorted into a hyped media frenzy, and the poor street dog is being driven into corners to quietly die.
Additionally, with harshly enforced sterilisation programmes, the sly and slow genocide of the street dog is happening before our very eyes. This crass model is copying the emotionally naïve and foolish behaviour of western societies fifty years ago, where the obedient pet is now the only role available to the dog. Their freedom and the right to live on the street, so bringing joy and decency to harsh realities, are being stolen away from them.”
As visitors navigate through the exhibition, they are invited to reflect on their own relationship with animals and nature and contemplate the profound lessons that can be gleaned from Indian art, culture, and heritage. In doing so, they embark on a journey of self-discovery, rekindling a sense of reverence for all living beings and reaffirming the interconnectedness of humanity and the natural world.
If you have any objection to this press release content, kindly contact pr.error.rectification@gmail.com to notify us. We will respond and rectify the situation in the next 24 hours.